[Algorithm] Leetcode - 1. Two Sum (JAVA)
Two Sum
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
You can return the answer in any order.
Constraints
2 <= nums.length <= 104-109 <= nums[i] <= 109-109 <= target <= 109- Only one valid answer exists.
Follow-up
Can you come up with an algorithm that is less than O(n2) time complexity?
Example
#1
Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [0,1]
Output: Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].
#2
Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
Output: [1,2]
#3
Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6
Output: [0,1]
내가 작성한 코드
문제를 보자마자 제일 먼저 들었던 풀이 방법이 이중 for 문으로 작성하는 방법이었다.
반복문을 통해서 두 수의 합이 target과 일치하면 return 하는 방식이다.
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] == target - nums[j]) {
return new int[] {i, j};
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
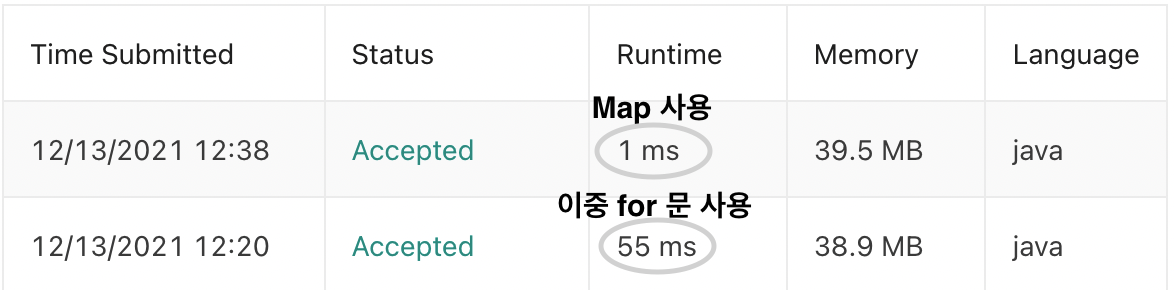
위의 풀이 방법은 시간복잡도가 O(N2) 이다.
Follow-up 의 내용과 같이 O(N2) 시간 복잡도보다 작은 알고리즘을 사용할 수 있지 않을까 고민해봤다.
Map 을 사용할 수 있지 않을까 생각해봤지만, 도무지 머리가 돌아가지 않아 다른 분들의 코드를 참고해서 풀어봤다.
다음 풀이 방법은 보수(target - 현재 수)와 Map을 이용한 풀이로, 시간 복잡도가 O(N) 이다.
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 현재 수(nums[i])의 보수가 있는지 확인
if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
// 있을 경우, 현재 수를 보수로 갖던 수의 index와 현재 index를 반환
return new int[] {map.get(nums[i]), i};
}
// 없을 경우, 현재 수의 보수 값을 key로 하고 현재 수의 index를 value로 하는 데이터 삽입
map.put(target - nums[i], i);
}
return new int[] {};
}
- 보수값(
target - 현재 값) 을 key로 하고 현재 index를 value로 하는 Map을 선언한다. - 반복문을 돌면서 Map에 현재 수(
nums[i])의 보수가 있는지 확인한다.- 있을 경우, 현재 수를 보수로 갖던 수의 index와 현재 index를 int 배열을 생성하여 반환한다.
- 없을 경우, Map에 현재 수의 보수 값을 key로 하고 현재 index를 value로 하는 데이터를 삽입한다.
- 주어진 nums 의 조합으로 target을 만들 수 없을 경우, 빈 int 배열을 반환한다.
이중 for 문으로 풀었을 경우와, Map을 이용하여 풀었을 경우, 아래 이미지와 같이 속도 면에서 확연하게 차이가 나는 것을 볼 수 있었다.
댓글남기기